Department of Computer Science | Institute of Theoretical Computer Science
Department of Computer Science | Institute of Theoretical Computer Science
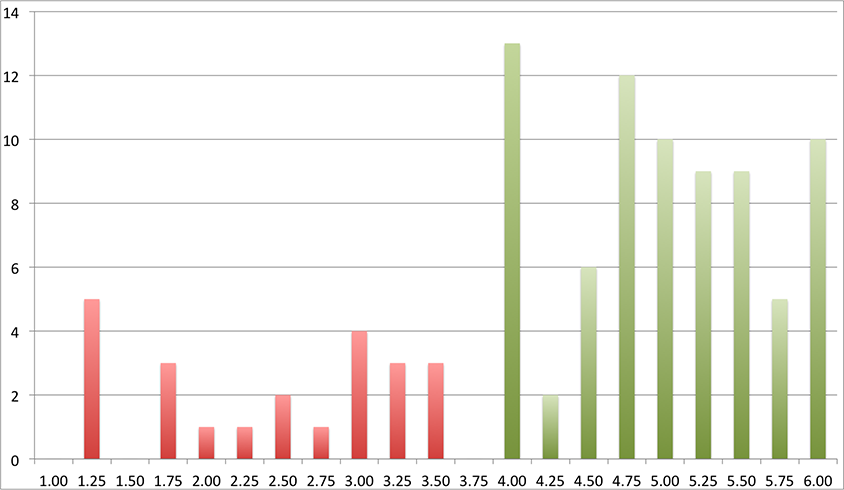
Exam Statistics (Feb 26, 2014)
Please do not
send email to any of the addresses below. Instead, for questions
on exercises use
the forums on the course homepage. For questions on the
course formalities etc.,
use algolab@lists.inf.ethz.ch.
First tutorial: Wednesday Sep 18,
17-19, CAB G 61
Tutorials: Wednesday, 17-19, CAB G 61
Problem of the week: Monday, 17-19, (CAB H 56, CAB H 57)
Office hours: Monday, 19-, CAB G15.2
see also: vvz.ethz.ch
The
objective of this course is to learn how to solve a problem given by a
textual description. This includes appropriate problem modeling,
choice of suitable (combinatorial) algorithms, and implementing them
using C/C++, STL, CGAL,
and BGL.
In this course
students learn how to solve algorithmic problems given by a textual
description. We assume knowledge of elementary algorithms and data
structures as they are typically taught on the Bachelor level; in
tutorials we introduce more advanced algorithms and the usage of some
standard libraries for combinatorial algorithms. Students are expected
to practice their skills by solving weekly exercises. For that they
will have to understand the problem setting, find an appropriate
modeling, choose suitable algorithms, and implement them using
C/C++, STL, CGAL,
and BGL.
The evaluation of the correctness and
efficiency of their solutions will be performed by an online-judge
which compiles the submitted source-code and runs it on a set of test
instances.
This course is a lab: Most of the time is spent by students working individually on the given problems.
In addition there is a
weekly tutorial. These tutorials are not lectures in the
classical sense. In particular we will not present theory and proofs
there. Instead we rely on the corresponding knowledge gained during
your Bachelor studies. The tutorials
serve
Occasionally we will work with algorithms and data structures that you may not have encountered during your Bachelor studies. Such algorithms and data structures will be properly introduced in the tutorials, with a focus on the application rather than on the underlying theory.
Each Wednesday after the tutorial we will hand out problem sets. You are expected to hand in solutions, using the online-judge, within one week.
The exercise hours on Mondays are devoted to a "Problem of the week". One such problem will be posed every week at this time. In order to score points for this problem, only solutions that are submitted within the two exercise hours are counted. The goal of this setup is to make students accustomed to exam conditions and provide an early feedback of where they stand.
Finally, the assistants will be available
at certain office hours. These offer a place to ask questions
and get help if you lack a necessary idea to solve a problem or if you
struggle with any other kind of course related
problem.
The grade of the course is solely based on the final exam. The exam takes place in a computer room, on two days, 6 hours each, during the examination session. On both days you have to solve problems similar to those given during the semester.
Solving elementary problems using C/C++, STL, and the algorithms and data structures listed here.
Tutorial
1: Introduction to the working environment and the submission
framework (online-judge) + Basics about how to program for this
lab.
Tutorial 2: BFS/DFS graph
traversals; general problem solving strategies: greedy and divide
& conquer
Tutorial 3: Dynamic programming
Tutorial 4: Introduction to
BGL
Tutorial 5: Network flow and matching algorithms in BGL
Tutorial 6: Introduction to CGAL
Tutorial 7: Proximity structures in CGAL
Tutorial 8: Linear and quadratic programming - theory & CGAL implementation
The exercises of these
weeks will be in the spirit of the
exam.
T. Cormen,
C. Leiserson, R. Rivest:
Introduction to Algorithms, MIT
Press, 1990.
J. Hromkovic,
Teubner:
Theoretische Informatik, Springer, 2004
(English: Theoretical Computer Science, Springer
2003).
J. Kleinberg, É. Tardos:
Algorithm
Design, Addison Wesley,
2006.
H. R. Lewis,
C. H. Papadimotriou:
Elements of the Theory of
Computation, Prentice Hall,
1998.
T. Ottmann, P. Widmayer:
Algorithmen
und Datenstrukturen, Spektrum,
2002.
R. Sedgewick:
Algorithms in
C++: Graph Algorithms, Addison-Wesley,
2001.